
共享内存指 (shared memory)在多处理器的计算机系统中,可以被不同中央处理器(CPU)访问的大容量内存。--百度百科
上述已经将共享内存的概念说的很清晰了,简单理解就是多个进程可共用一片存储内存。
Linux已经提供了共享内存的接口,本文主要简单介绍此接口使用方法及使用实例。
接口说明设置共享存储标识符:
设定共享内存的标识符,用于读写时唯一许可。
/**
* @brief: returns the identifier of the System V shared memory
* segment associated with the value of the argument key.
*
* @param - key: identification of the IPC
* @param - size: the size of shared memory usage
* @param - shmflg: If shmflg specifies both IPC_CREAT and IPC_EXCL
* and a shared memory segment already exists for key, then shmget()
* fails with errno set to EEXIST.
*
* @return On success, a valid shared memory identifier is returned.
* On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate the error.
*/int shmat(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg)
将共享字段链接到地址空间
设定共享内存字段在系统的存储地址。
/**
* @brief: shmat() attaches the System V shared memory segment
* identified by shmid to the address space of the calling process.
*
* @param - shmid:
* @param - shmaddr: the addr of the System V shared memory
* @param - shmflg:
*
* @return On success, shmat() returns the address of the attached
* shared memory segment;
* on error, (void *) -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate
* the cause of the error.
*/void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg)
取消共享地址映射
当共享内存使用完毕后,调此接口会结束共享内存与指定的系统地址的映射关系。这里并未从系统中删除标识符,该标识符一直存在直至某个进程带IPC_RMID命令调用shmctl特地删除它为止。
/**
* @brief: detaches the shared memory segment located at the
* address specified by shmaddr from the address space of the calling
* process.
*
* @param - shmaddr: the addr of the System V shared memory
*
* @return On success, shmdt() returns 0;
* on error -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate the cause of
* the error.
*/int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);
共享内存多种操作
类似于驱动ctrl函数,即传入不同的命令可执行不同的操作。cmd可选择IPC_STAT/IPC_SET/IPC_RMID/SHM_LOCK/SHM_UNLOCK。
IPC_STAT 将与shmid关联的内核数据结构中的信息复制到buf所指向的shmid_ds结构中。
IPC_SET 将buf指向的shmid_ds结构的一些成员的值写入与这个共享内存段相关联的内核数据结构,同时更新它的shm_ctime成员。
IPC_RMID 标记要销毁的共享内存。只有在最后一个进程将它分离之后,共享内存才会被销毁。
SHM_LOCK 防止读取共享内存。
SHM_UNLOCK 解锁共享内存,允许它被读取出来。
/**
* @brief: performs the control operation specified by cmd on the
* System V shared memory segment whose identifier is given in shmid.
*
* @param - shmid:
* @param - cmd:
* @param - buf:
*
* @return A successful IPC_INFO or SHM_INFO operation returns the
* index of the highest used entry in the kernel's internal array recording
* information about all shared memory segments. (This information
* can be used with repeated SHM_STAT or SHM_STAT_ANY operations
* to obtain information about all shared memory segments on the system.)
* A successful SHM_STAT operation returns the identifier of the shared
* memory segment whose index was given in shmid. Other operations
* return 0 on success.
* On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
*/int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf)
功能: 使用共享内存设计两个读写进程,实现跨进程通信。演示: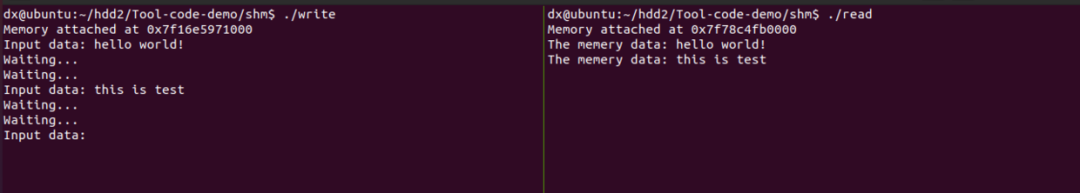
本文主要接收共享内存接口的简单使用实例,其可通过shmctl传输不同的指令实现比较高级的用法,例如权限限制。其中共享内存也可以配合其他机制实现一套比较好用的通信策略,后续可以玩一玩。
代码
read.cpp
#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/shm.h>#include "common.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ int shmid, running = 1; void *shm = NULL; struct ShmData *pShareData = NULL;
shmid = shmget((key_t)SHM_NAME, sizeof(struct ShmData), 0666|IPC_CREAT); if (shmid == -1) { printf("shmget failed! "); exit(0); }
shm = shmat(shmid, 0, 0); if (shm == (void*)-1) { printf("shmat failed! "); exit(0); } printf("Memory attached at %p ", shm);
pShareData = (struct ShmData *)shm; pShareData->flag = 0;
while (running) { if (pShareData->flag) { printf("The memery data: %s", pShareData->data); sleep(rand() % 3); pShareData->flag = 0;
if (!strncmp(pShareData->data, "end", 3)) { running = 0; }
} else { sleep(1); } }
printf("Over! "); if (shmdt(shm) == -1) { printf("shmdt failed! "); exit(0); }
if (shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) == -1) { printf("shmctl failed! "); exit(0); }
return 0;}
write.cpp
#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/shm.h>#include "common.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ int shmid, running = 1; char buffer[DATA_SIZE+1] = {0}; void *shm = NULL; struct ShmData *pShareData = NULL;
shmid = shmget((key_t)SHM_NAME, sizeof(struct ShmData), IPC_EXCL); if (shmid == -1) { printf("shmget failed! "); exit(0); }
shm = shmat(shmid, (void*)0, 0); if (shm == (void*)-1) { printf("shmat failed! "); exit(0); } printf("Memory attached at %p ", shm);
pShareData = (struct ShmData *)shm; //pShareData->flag = 0;
while (running) { while (pShareData->flag == 1) { sleep(1); printf("Waiting... "); }
printf("Input data: "); fgets(buffer, DATA_SIZE, stdin); strncpy(pShareData->data, buffer, DATA_SIZE); pShareData->flag = 1;
if (strncmp(buffer, "end", 3) == 0) { running = 0; } }
if (shmdt(shm) == -1) { printf("shmdt failed! "); exit(0); } sleep(2);
return 0;}
最后
用心感悟,认真记录,写好每一篇文章,分享每一框干货。愿每一篇文章不负自己,不负看客!
更多文章内容包括但不限于C/C++、Linux、开发常用神器等,可进入开源519公众号聊天界面回复“文章目录” 或者 菜单栏选择“文章目录”查看。

本文摘自 :https://blog.51cto.com/u

