原型模式(Prototype)
原型模式是一种创建型设计模式,其功能为复制一个运行时的对象,包括对象各个成员当前的值。而代码又能保持独立性。
场景
举例
假设这样一个场景,孙悟空出世,在花果山经历与猴孙的生死离别后,拜菩提老祖为师。历经多年,学的一身本领。此时的悟空拔出一个毫毛,变出一个自己。
分析
此时悟空变出的另一个自己,自然要与现在的年龄、身高、体重等多个参数一致。如果不加设计,这些代码可能散落在客户端函数。假如过了十年继续施展分身,又需重新增加这些代码。日积月累,这些终将成为晦涩而又难以维护的“一坨”。
实现
对于上述场景就有必要引入原型模式,原型模式的设计也是比较简单的。只需要在类的设计时增加一个clone接口,用于返回当前对象this指针。客户端在使用时,只需要对象的clone接口,就能拿到当前对象的各个成员值。
类图
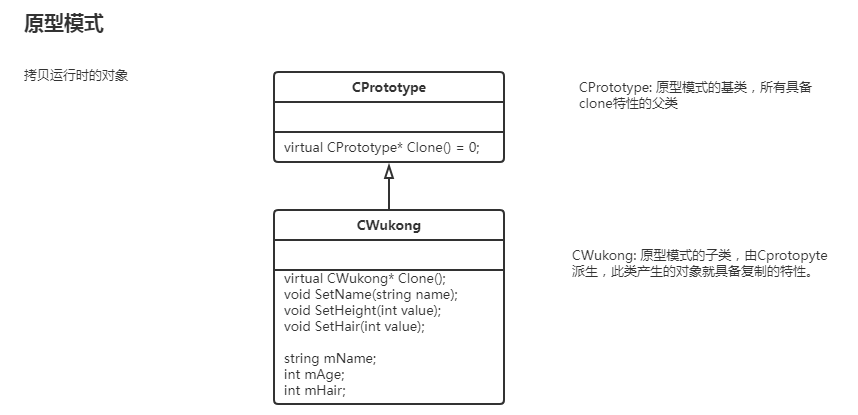 原型模式
原型模式
通过原型模式基类规范具备复制接口的子类实现。
源码
#include <iostream>#include <string>
using namespace std;
class CPrototype{public:
CPrototype() {}
~CPrototype() {}
virtual CPrototype* Clone() = 0;};
class CWukong : CPrototype{public: CWukong() : mAge(0), mHeightCM(100), mHair(10000), mLockRing(0), mFightCapacity (20) {
}
CWukong(CWukong *rhs) { mName = rhs->mName; mAge = rhs->mAge; mHeightCM = rhs->mHeightCM; mHair = rhs->mHair; mLockRing = rhs->mLockRing; mFightCapacity = rhs->mFightCapacity; }
virtual ~CWukong() {}
void SetName(string value) { mName = value; }
void AddAge(int value) { mAge += value; }
void SetHeight(int value) { mHeightCM = value; }
void SetHair(int value) { mHair = value; }
void PutLockRing() { mLockRing = 1; }
void RemoveLockRing() { mLockRing = 0; }
void SetFightCapacity(int value) { mFightCapacity = value; }
string GetName() { return mName; }
int GetAge() { return mAge; }
int GetHeight() { return mHeightCM; }
int GetHair() { return mHair; }
int GetLockRing() { return mLockRing; }
int GetFightCapacity() { return mFightCapacity; }
CWukong* Clone(){return new CWukong(*this); }
private:string mName;int mAge;int mHeightCM;int mHair;bool mLockRing;int mFightCapacity;};
static void learn_skills(CWukong *pMonkey){//After 11 years of study, Wukong's parameters change pMonkey->SetName("Wukong.Sun"); pMonkey->AddAge(11); pMonkey->SetHeight(150); pMonkey->SetFightCapacity(80);}
static void show_params(CWukong *pMonkey){cout << ">> " << pMonkey->GetName() << endl;cout << "Age: " << pMonkey->GetAge() << endl;cout << "Height(cm): " << pMonkey->GetHeight() << endl;cout << "Hair: " << pMonkey->GetHair() << endl;cout << "LockRing: " << pMonkey->GetLockRing() << endl;cout << "FightCapacity: " << pMonkey->GetFightCapacity() << endl;cout << " " << endl;}
int main (int argc, char *argv[]){ CWukong *theWukong = new CWukong();//Before Learning, show paramscout << "Before Learning" << endl; show_params(theWukong);
//At the age of five, he went to learn skills theWukong->AddAge(5); theWukong->SetHeight(120); learn_skills(theWukong);//Return after Learning, show params show_params(theWukong);
//Show multitasking skillscout << "Clone Wukong" << endl; CWukong *theWukong2 = theWukong->Clone(); show_params(theWukong2);
delete theWukong2;delete theWukong;return 0;}
输出
Before Learning>> Age: 0Height(cm): 100Hair: 10000LockRing: 0FightCapacity: 20
>> Wukong.SunAge: 16Height(cm): 150Hair: 10000LockRing: 0FightCapacity: 80
Clone Wukong>> Wukong.SunAge: 16Height(cm): 150Hair: 10000LockRing: 0FightCapacity: 80
实现流程
- 首先需要在父类定义 克隆(clone) 纯虚接口,子类需要在此接口中返回新创建的子类对象。
- 子类中,增加一个以此类对象为参数的构造函数。用于保存当前所有成员变量值到新创建的对象中。
- 子类的克隆接口,创建新的对象时,需要显示调用具备子类对象参数的构造函数。保证新的对象中,所有的成员都被初始化。
总结
- 原型模式能够克隆一个对象,而类之间无需耦合。
- 客户代码在复制复杂的对象时,也更加方便。
- 此接口可重复使用,让代码逻辑更加清晰易懂。
-
本文摘自 :https://blog.51cto.com/u

