使用栈实现一个队列,需要弄清楚栈和队列的区别:
栈:先进后出;
队列:先进先出。
实现思路:
1)通过两个栈(pushStack / popStack)对倒,确保 popStack 栈的出栈顺序与队列出列一致。
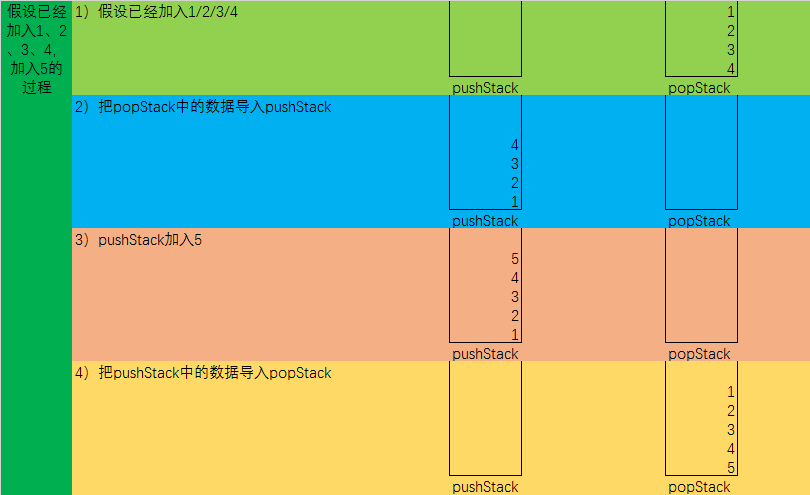
2)核心难点在加入队列操作,假设队列中已经加入1、2、3、4,加入5的过程:
2.1)假设已经加入1/2/3/4
2.2)把popStack中的数据导入pushStack
2.3)pushStack加入5
2.4)把pushStack中的数据导入popStack
流程示意图如下:
实现代码:
import java.util.Stack; public class QueueWithStack<T> { /** * Test 测试代码 */ public static void main(String[] args) { QueueWithStack<Integer> queue = new QueueWithStack<>(); queue.add(1); System.out.println("入队列:1"); queue.add(2); System.out.println("入队列:2"); queue.add(3); System.out.println("入队列:3"); queue.add(4); System.out.println("入队列:4"); System.out.println("出队列:" + queue.pop()); System.out.println("出队列:" + queue.pop()); queue.add(5); System.out.println("入队列:5"); queue.add(6); System.out.println("入队列:6"); System.out.println("===================="); while (false == queue.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("出队列:" + queue.pop()); } System.out.println("队列内元素个数:" + queue.size()); } // 入栈是,将数据写入该集合,然后在推向pop集合。 private Stack<T> pushStack = null; // 出站时,读取该集合 private Stack<T> popStack = null; public QueueWithStack() { pushStack = new Stack<>(); popStack = new Stack<>(); } public boolean isEmpty() { return popStack.isEmpty(); } public int size() { return popStack.size(); } public void add(T t) { while (false == popStack.isEmpty()) { T val = popStack.pop(); pushStack.push(val); } pushStack.add(t); while (false == pushStack.isEmpty()) { T val = pushStack.pop(); popStack.push(val); } } /** * 从队列中取出数据,并从队列中移除数据 */ public T pop() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty."); } return popStack.pop(); } /** * 获取栈顶元素,但不会从队列中移除数据 */ public T peek() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty."); } return popStack.peek(); } }
打印结果:
入队列:1 入队列:2 入队列:3 入队列:4 出队列:1 出队列:2 入队列:5 入队列:6 ==================== 出队列:3 出队列:4 出队列:5 出队列:6 队列内元素个数:0
基础才是编程人员应该深入研究的问题,比如:
1)List/Set/Map内部组成原理|区别
2)mysql索引存储结构&如何调优/b-tree特点、计算复杂度及影响复杂度的因素。。。
3)JVM运行组成与原理及调优
4)Java类加载器运行原理
5)Java中GC过程原理|使用的回收算法原理
6)Redis中hash一致性实现及与hash其他区别
7)Java多线程、线程池开发、管理Lock与Synchroined区别
8)Spring IOC/AOP 原理;加载过程的。。。
【+加关注】。
本文摘自 :https://blog.51cto.com/u

